
Next: O2, O3, O3-
Up: Applications
Previous: The electronic spectrum of
Toggle Background
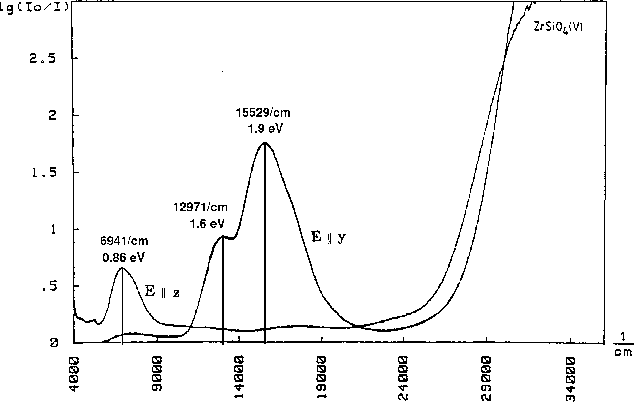
Vanadium doped zircon (ZrSiO4:V) shows a deep blue colour and provides
a superior thermal and chemical stability making it an
important industrial pigment. The colour is given by
the following absorption spectrum:
Due to the low level of doping it is not possible to extract the
crystal structure by indirect spectroscopic methods. It remains the
question: What is the chromophore and what
is the location of vanadium in the zircon host lattice?
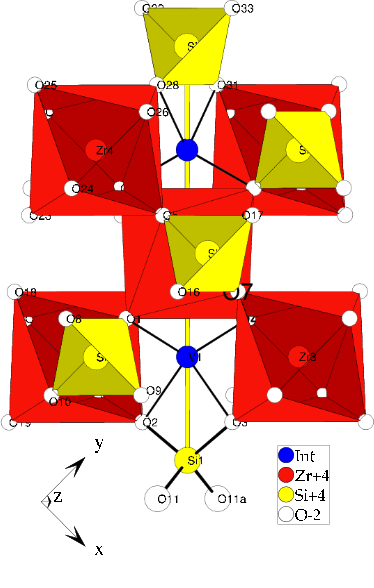
The zircon crystal structure is known as:
| view on the (001) plane |
|
view on the (111) plane |
 |
|
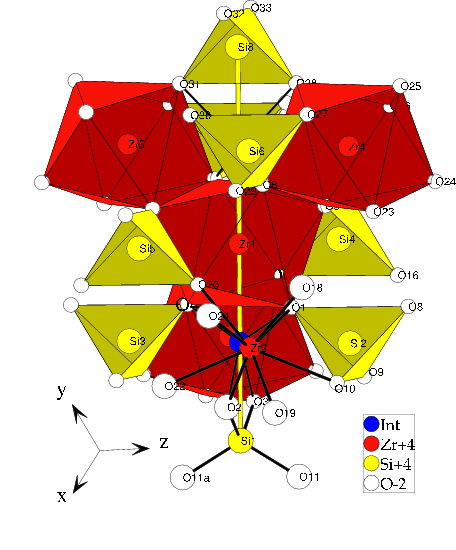 |
The label "Int" marks an interstitial site the zircon crystal structure
provides. Finally there are three possible locations for the vanadium:
- Replace zircon
- Replace silicon
- Reside at the insterstitial site
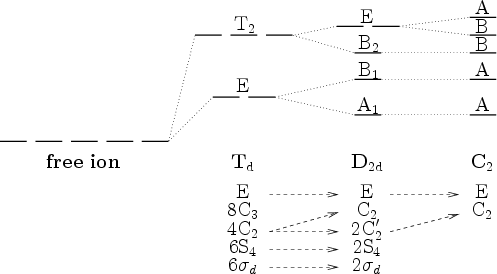
Ligand-Field Theory
- V electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d5
- V4+ electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d1
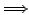 3d1 ion
3d1 ion
- "Standard"-splitting:
- Allowed electronical transitions:
| Site |
Symmetry |
# transitions |
| V@Zr, V@Si |
D2d |
one ore two * |
| V@Int |
C2 |
four |
* depending on ground state
Quantum Chemical Calculation
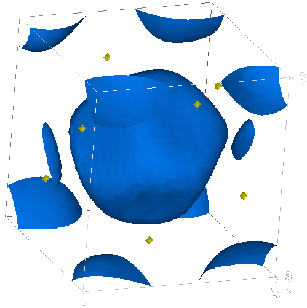
- V4+ ion in Madelung Potential
- Approximation by about 500 point charges located at the regular places
of the ions
- Least square fit
- Optimization of charges within a sphere of 4.5 Å radius
around the vanadium atom.
| Madelung potential at V4+ |
Simulated spectrum |
Expected excitations |
 |
 |
| |
|
f /10-8 |
| State |
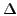 E / eV
5 E / eV
5 |
x = y |
z |
| X 2A1 |
0.00 |
-- |
-- |
| 1 2E |
0.04 |
0.04 |
-- |
| 1 2B1 |
0.05 |
-- |
-- |
| 1 2B2 |
0.59 |
-- |
1.3 |
|
 |
 |
| |
|
f /10-8 |
| State |
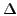 E / eV
6 E / eV
6 |
x = y |
z |
| X 2B1 |
0.00 |
-- |
-- |
| 1 2A1 |
0.11 |
-- |
-- |
| 1 2B2 |
0.17 |
-- |
-- |
| 1 2E |
0.47 |
2.4 |
-- |
|
 |
 |
| |
|
f /10-7 |
| State |
 E / eV 7 E / eV 7 |
x |
y |
z |
| X 2A |
0.00 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 1 2B |
0.86 |
-- |
2.3 |
6.3 |
| 1 2A |
1.23 |
2.0 |
-- |
-- |
| 2 2B |
1.27 |
-- |
0.2 |
4.2 |
| 2 2A |
1.50 |
27 |
-- |
-- |
|
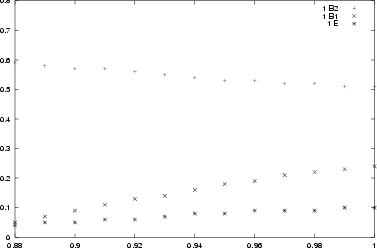
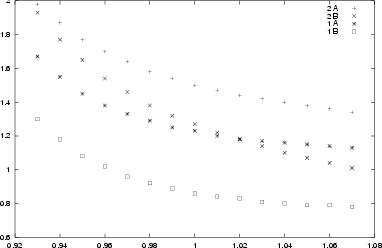
The crystal field at the zircon and silicon sites is highly spherically
symmetric and there is only little energy splitting of the d-orbitals.
For the interstitial site however the field is highly non-symmetric
yielding one energy lowered d-orbital. Consequently the excitation
energies are largest for this case.
To summerize: The simultated spectra strongly suggest that
the observed absorption spectrum is caused
by vanadium ions located at the interstitial sites
[13].
Footnotes
- ... zircon4
- In cooperation with
A. Niesert, Institute for Anorganic Chemistry, University of Bonn and
M. Jansen, MPI for Solid State Research, Stuttgart and
S. Siggel, TU Berlin, Institute for Applied Geology, Berlin
- ... eV5
- at enlargement factor 0.88, corresponding to expected
collapse of the Zr-site due to different ionic radii
- ... eV6
- at enlargement factor 1.08, corresponding to expected
expansion of the Si-site due to different ionic radii
- ... eV7
- at enlargement factor 1, corresponding to
EXAFS results from S. Siggel


Next: O2, O3, O3-
Up: Applications
Previous: The electronic spectrum of
Michael Hanrath
2008-08-13